Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is one of the most practical ways to deploy AI safely in production—especially for voice agents. In this guide, you’ll learn how to build a secure, hallucination-resistant RAG API in n8n 2.2.6, suitable for ElevenLabs or any conversational frontend.
This walkthrough is based on a production-hardened n8n workflow and focuses on clarity, reliability, and cost control, not demos.
What This RAG System Does
By the end, you will have an API that:
- Accepts a user question over HTTP
- Authenticates and validates the request
- Retrieves relevant knowledge from Pinecone
- Generates grounded answers with OpenAI
- Returns clean, voice-safe JSON responses
This design avoids hallucinations, limits token spend, and is safe to expose publicly.
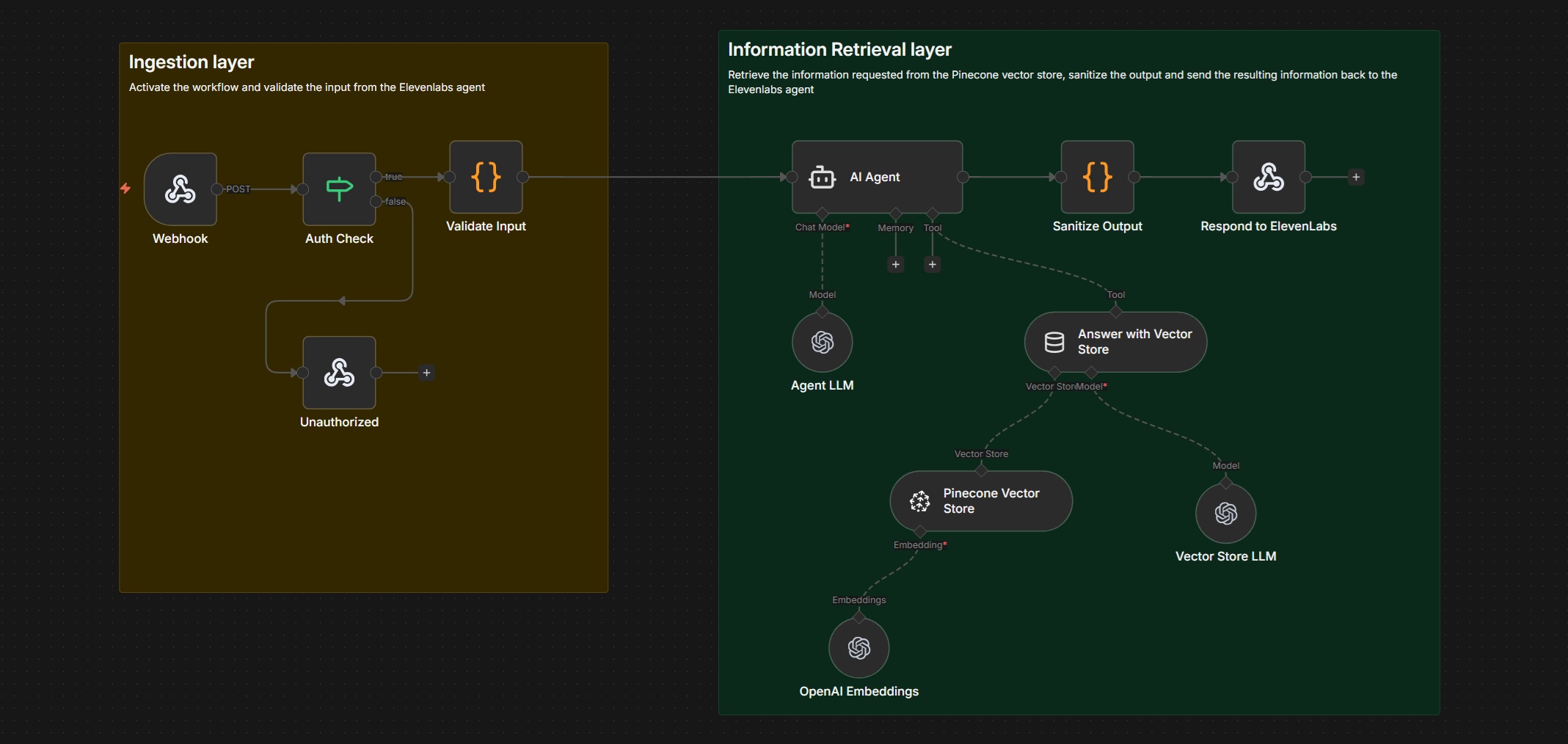
High-Level Architecture
Execution flow:
Webhook → Auth Check → Input Validation → AI Agent → Vector Search (Pinecone) → Answer Generation → Output Sanitization → HTTP Response
Each stage exists to solve a real production problem: security, data quality, accuracy, or cost.
Step 1: Create the Webhook API Endpoint
Start with an n8n Webhook node. This node exposes the public HTTP endpoint used by ElevenLabs or another client.
Configuration:
- Method: POST
- Response Mode: Respond to Webhook
Expected request body:
{
"question": "What is the return policy for Velocity Cycles?"
}
This webhook is the only public-facing surface of the workflow.
Step 2: Secure the Endpoint with Authentication
Immediately add an IF node after the webhook.
Why this matters:
- n8n does not provide built-in auth or rate limiting
- Public endpoints without auth will get abused
Implementation:
- Require a custom header such as
x-agent-key - Compare it to an environment variable (for example,
ELEVENLABS_AGENT_KEY)
If the check fails, return a 401 Unauthorized response and stop execution. This alone saves you real money.
Step 3: Validate and Normalize User Input
Add a Code node to validate incoming requests before any AI calls.
Validation rules:
questionmust exist- Must be a string
- Length capped (e.g. 500 characters)
- Reject empty or trivial input
This step prevents token abuse, malformed payloads, and unnecessary embedding or LLM calls.
Step 4: Configure the AI Agent (RAG Orchestrator)
Add a LangChain AI Agent node. The agent does not answer directly—it decides how to answer.
Lock the agent down with a strict system message:
- Always query the vector store
- Use only retrieved context
- Refuse when no relevant data exists
- Output structured JSON only
This is the single most important step for preventing hallucinations.
Step 5: Attach the OpenAI Chat Model
Connect an OpenAI Chat Model node to the agent.
Recommended settings:
- Model: gpt-4.1-mini
- Temperature: 0.2
- Max tokens: 250
Low temperature ensures predictable output. Hard token limits control latency and cost—critical for voice workflows.
Step 6: Enable Retrieval with the Vector Store Tool
Attach the Vector Store Tool node to the agent.
Configuration tips:
- Retrieve a small number of results (top 5)
- Explicitly instruct the tool to answer only from retrieved documents
At this point, the workflow becomes a true RAG pipeline, not a chatbot.
Step 7: Configure Pinecone as the Knowledge Store
Add a Pinecone Vector Store node.
Key settings:
- Index:
n8n-rag-agent - Namespace:
ragagent
This index holds your embedded knowledge base—product docs, FAQs, policies, or internal references.
Step 8: Add OpenAI Embeddings for Semantic Search
Attach an OpenAI Embeddings node to Pinecone.
This node converts the user’s question into a vector, enabling semantic similarity search based on meaning rather than keywords.
Step 9: Generate a Grounded Answer
With relevant documents retrieved, the agent generates an answer using the OpenAI chat model.
Enforced output format:
{
"answer": "Short, spoken answer",
"confidence": "high | medium | low"
}
If no relevant documents are found, the agent must respond with:
“I don’t have that information.”
This explicit refusal is essential for voice safety and user trust.
Step 10: Sanitize Output for Voice
Add a Code node to sanitize the final response.
This step removes:
- Markdown
- Line breaks
- Formatting artifacts
The result is clean, speakable text that works reliably with ElevenLabs and other text-to-speech engines.
Step 11: Return the HTTP Response
Finish with a Respond to Webhook node.
Return:
- HTTP 200
- JSON containing
answerandconfidence
This response is consumed directly by the voice layer.
Why This Architecture Works in Production
This RAG system is:
- Secure: authenticated entry point
- Accurate: retrieval-first, no guessing
- Cost-controlled: capped tokens and early exits
- Voice-safe: sanitized, short responses
- Maintainable: clear separation of concerns
It is safe to expose publicly and scales predictably.
Adding System Resiliency : Implementing Production Enhancements
This chapter extends the base workflow with caching, observability, ingestion, and deterministic behavior. Each enhancement is optional, but together they move the system from reliable to enterprise-grade.
1. Add Response Caching (Cost & Latency Reduction)
Problem: Repeated questions trigger repeated vector searches and LLM calls.
Solution: Cache answers using workflow static data or Redis.
Implementation:
- Hash the normalized question
- Check cache before calling the AI Agent
- If cache hit → return response immediately
Impact:
- 40–70% cost reduction on common queries
- Faster responses for voice agents
2. Enforce Similarity Thresholds (Accuracy Guardrail)
Problem: Top-K retrieval alone can return weak matches.
Solution: Add a similarity score cutoff.
Implementation:
- Inspect Pinecone similarity scores
- Reject results below a threshold (for example, 0.75)
- Force an explicit “I don’t have that information” response
Impact:
- Eliminates confident but incorrect answers
- Improves user trust
3. Add Structured Observability (Debuggability)
Problem: Without logs, RAG failures are invisible.
Solution: Log every request and retrieval decision.
What to log:
- Question hash
- Cache hit or miss
- Retrieved document IDs
- Similarity scores
- Token usage
- End-to-end latency
Impact:
- Faster debugging
- Clear insight into retrieval quality
4. Build a Document Ingestion Workflow
Problem: Knowledge bases must evolve.
Solution: Create a separate ingestion workflow that:
- Accepts documents (PDF, markdown, text)
- Chunks content
- Generates embeddings
- Upserts vectors into Pinecone
Impact:
- Keeps answers current
- Removes manual re-indexing
5. Move Toward Deterministic RAG (Optional)
Problem: Agents introduce variability.
Solution: Replace the agent with a fixed RAG chain:
- Embed question
- Retrieve documents
- Inject context into a fixed prompt
- Generate answer
Impact:
- Maximum predictability
- Easier compliance and auditing
Final Outcome
With these enhancements applied, the system becomes:
- Highly cost-efficient
- Observable and debuggable
- Resistant to hallucinations
- Easy to extend and maintain
This architecture scales cleanly from small pilots to high-volume production voice systems.